AutoFix: Fixing the Specification
While most debugging techniques focus on patching implementations, there are numerous bugs whose most appropriate corrections consist in fixing the specification to prevent invalid executions — such as to define the correct input domain of a function. AutoFix also includes a fully automatic technique that fixes bugs by proposing changes to contracts.Let us briefly demonstrate how AutoFix propose fixes to contracts using an example. The example targets a bug of routine (method)
duplicate
in class CIRCULAR, which is the standard Eiffel
library implementation of circular array-based lists. To understand the
bug, Figure 1 illustrates a few details of CIRCULAR's
API. Lists are numbered from index 1
to index count (an attribute denoting the list length),
and include an internal cursor that may point to any element of the list.
Routine duplicate takes a single integer argument n,
which denotes the number of elements to be copied; called on a list object
list, it returns a new instance of CIRCULAR with
at most n elements copied from list starting from the position
pointed to by cursor. Since we are
dealing with circular lists, the copy wraps over to the first element. For
example, calling duplicate(3) on the list in Figure 2
returns a fresh list with elements <C,D,A> in
this order.
1 class
|
|
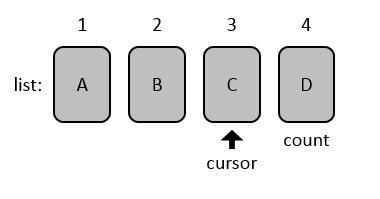 |
Figure 1. Some
implementation details of CIRCULAR.
|
|
Figure 2. A circular list of
class CIRCULAR:the internal cursor points to the element C at index 3. |
duplicate is straightforward: it creates a fresh CIRCULAR
object Result (line 9 in Figure 1); it iteratively copies n
elements from the current list into Result;
and it finally returns the list attached to Result.
The call to the creation procedure (constructor) make on line 9 allocates space for a list with
count elements; this is certainly sufficient, since Result
cannot contain more elements than the list that is duplicated. However,
CIRCULAR’s creation procedure make
includes a precondition (line 4 in Figure 1) that only allows allocating
lists with space for at least one element (require m >= 1).
This sets off a bug when duplicate is called on an empty list: count
is 0, and hence the call on line 9 triggers a violation of make’s precondition.
Testing tools such as AutoTest detect this bug automatically by providing
a concrete test case that exposes the discrepancy between implementation and specification.
|
|
|
| (a) Patching the implementation. | (b) Strengthening the specification. | (c) Weakening the specification. |
| Figure 3: Three different fixes for the bug of Figure 1. | ||
How should we fix this bug? Figure 3 shows three different possible repairs, all of which AutoFix can generate completely automatically. An obvious choice is patching
duplicate’s implementation as shown in
Figure 3a. A different, straightforward specification fix
is shown in Figure 3b: adding a
precondition to duplicate that only allows calling
it on non-empty lists (Figure 3b). A more general fix, also
generated by AutoFix, weakens make’s precondition
as shown in Figure 3c. This is arguably the most appropriate
correction to the bug of duplicate: it is very simple, it fixes
the specific bug as well as similar ones originating in creating
an empty list, and it does not invalidate any clients
of CIRCULAR’s API. AutoFix ranks the fix in Figure
3c higher than the other fixes.